Lumbar Herniated Disc
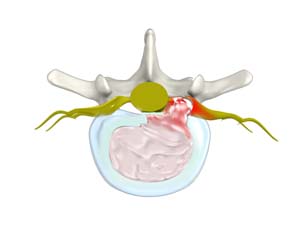
What is a Lumbar Herniated Disk?
A herniated disk is a condition in which the outer fibers (annulus) of the intervertebral disk are damaged, causing the soft inner material of the nucleus pulposus to rupture out of its space. It is the most common cause of lower back pain and pain that radiates down the leg (radiculopathy).
Symptoms of a Lumbar Herniated Disk
The most common symptom of a herniated disc is pain. The pain can vary from mild to debilitating depending on the degree of pressure exerted on the sciatic nerve. Patients having nerve compression experience other symptoms such as:
- Pain in the buttock area and leg
- Sharp, intense, shooting pain down the leg
- Numbness, burning or tingling sensation in the leg or foot
- Weakness of the leg or foot
- Lower back pain that radiates down the buttock and leg
- Pain that increases with coughing, sneezing or straining
- Pain that increases with bending backward and with prolonged sitting or standing
Diagnosis of Herniated Disc
Sciatica/herniated disc is diagnosed by reviewing your complete medical history, performing a physical examination and assessment of neuromuscular functions. Advanced imaging such as MRI, CT scan, CT scan with myelogram, electromyogram, and nerve conduction tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis of nerve compression/sciatica.
Treatment of Sciatica/Herniated Disc
Herniated disc can be treated with conservative approaches such as physical exercises, over-the-counter drugs, ice or hot packs, prescription medications, epidural steroid injections, massages, and manual manipulation. These treatments do not make the herniated disc go away, but provides a means for your body to cope while your body heals the herniated disc. In many cases, a MRI done many months after a herniated will not show the herniated disc any more.
In some cases, surgery may be recommended to treat the underlying condition.
